Machinery Safety and Safety Equipment
Machinery safety is the concept of designing machinery and constructing structures and mechanisms in a manner that prevents disasters even if a machine breaks down or when an operator makes a mistake. This could also be described as an approach that enables machines to be used safely even in the event of mechanical troubles or human error.
Reducing risks under this concept of machinery safety requires the use of safety devices.
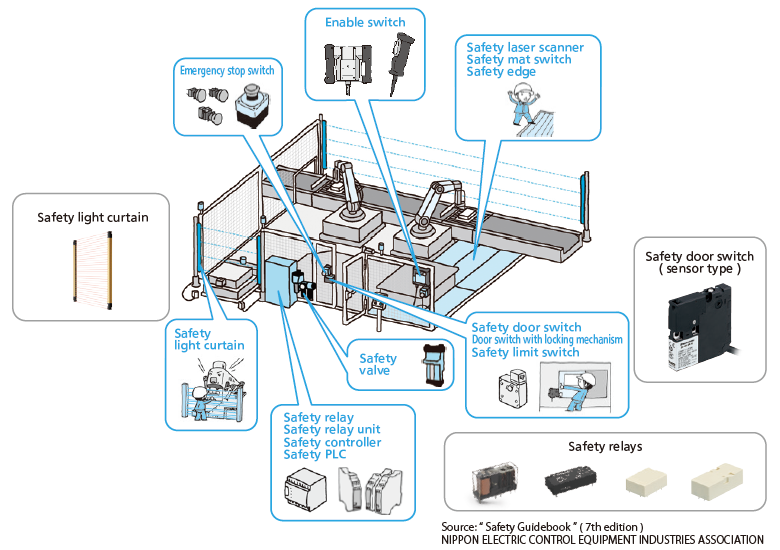
- The term "safety equipment" refers to equipment designed to enable safe operation and maintenance of machinery equipment at factory facilities, chemical plants, and other locations.
- The purpose of safety equipment is to ensure the safety of workers in the event of machine failure or malfunction. As such, safety equipment differs from ordinary products and requires specific safety functions.
- The following are used in safety-related electrical control systems: Safety switches, Emergency stop push buttons, Safety light curtains, Safety relay modules, and Safety relays, etc.
This document introduces safety standards and specific applications with a focus on "safety relays," which are required to ensure machinery safety.
Product examples of safety equipment
International Safety Standards
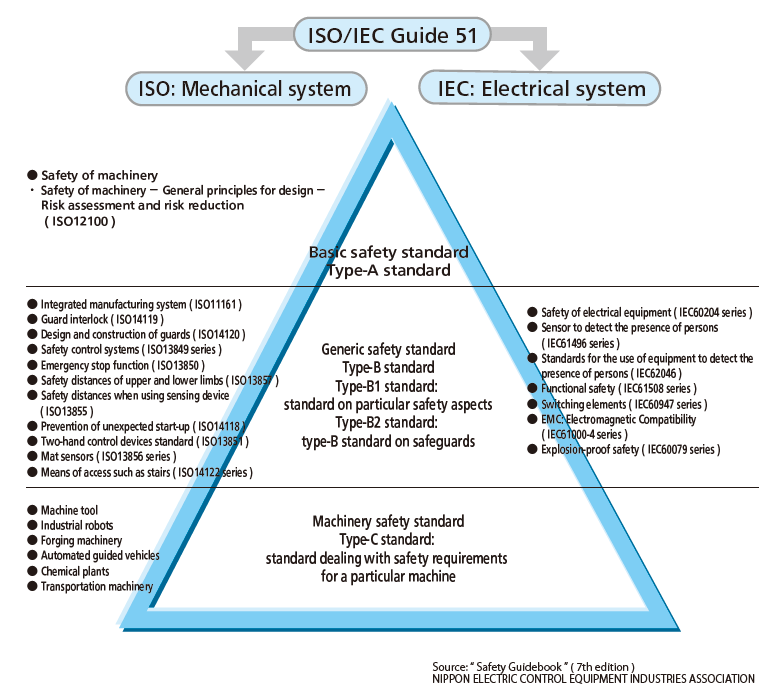
System of international standards
International standards for machinery safety are created by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), which conducts international standardization primarily in the fields of electric/electronic technologies, and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), which conducts international standardization including fields other than electric/electronic technologies (machinery, management, etc.) . In particular, the ISO/IEC Guide 51 is published to indicate the concepts common to safety standards issued by each organization.
Design Considerations for Safety Systems
Safety standards and safety relays
| Performance Level (PL) |
Probability of Dangerous Failure per Hour (PFHd) 1/h |
| a | 10-5 < PFH < 10-4 |
| b | 3 x 10-6 < PFH < 10-5 |
| c | 10-6 < PFH < 3 x 10-6 |
| d | 10-7 < PFH < 10-6 |
| e | 10-8 < PFH < 10-7 |
| Safety Integrity Level (SIL) |
Probability of Dangerous Failure per Hour |
| No special safety requirement |
10-5 < PFH < 10-4 |
| 1 | 3 x 10-6 < PFH < 10-5 |
| 1 | 10-6 < PFH < 3 x 10-6 |
| 2 | 10-7 < PFH < 10-6 |
| 3 | 10-8 < PFH < 10-7 |
▶ Safety function failure probability is determined by the combination of the parts with safety functions!
Safety relays with forcibly guided structures themselves are originally neither ISO13849-1 (PL) nor IEC62061 (SIL) compliant. For application producers who require a safety standard (e.g., PLC/safety light curtains) , B10/B10d values can be provided to prove the failure probability of safety functions.
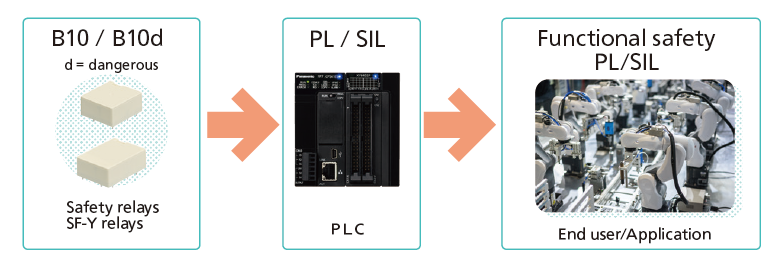
- B10 refers to the average number of cycles before 10% of parts or systems failure (including both safe and dangerous failures).
- B10d refers to the average number of cycles before 10% of parts or systems failure in a dangerous side.
Note) When a B10 value is available, the B10d value may in some cases be calculated by doubling the B10 value.
| Load | B10d |
| AC1 230 V 6 A | 2 M |
| AC15 230 V 5 A | 35 k |
| DC1 24 V 6 A | 2 M |
| DC13 24 V 4 A | 500 k |
| DC13 24 V 2 A | 1.6 M |
Why are safety relays necessary?
There is no obligation to install safety relays in safety equipment. However, installing safety relays facilitates designing safety equipment, simplifies the approval process, and ensures that safety equipment is deployed on time.
| Item | General relay | Safety relay (Forcibly guided contact structure) |
| Diagnostic coverage & Average DC: Diagnostic Coverage & DC avg |
From 0% Board designers need to increase the DC value using circuits to reach the required PL and SIL. |
99% Enables board designers to reach the required PL and SIL more easily. |
| Mean cycles to failure (B10/B10d) |
Very little information Even if there is only B10. |
The measurement method of B10d is compliant with DIN EN 61810-2-1. |
| Coil failure detection with safe feedback contacts |
Board designers need to take appropriate measures. |
Compatible with relay structure |
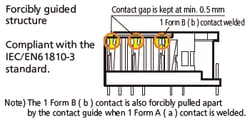
| Failure detection with safe feedback contacts (contact welding) |
Not compatible | Compatible |
| Other contact gaps at the time of contact welding |
Failures due to contact welding cannot be detected due to insufficient contact gap. |
Securing of contact gap min. 0.5 mm ensures reliable detection of contact welding and other factors. Also, since it is compliant with IEC61810-3, it is ideal for safety circuit design. |
| Price level | Low price However, other parts and systems are needed in order to achieve machinery safety, which results in additional costs. |
Slightly higher price (Due to additional design to ensure compatibility with forcibly guided structures, such as multiple contacts and contact GAP securing, etc.) |
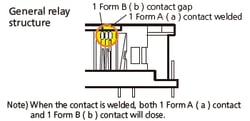
Differences between safety relays and general relays
| Safety relay | General relay | |
| Structure | 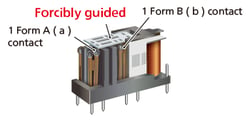 |
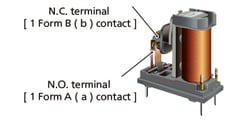 |
| Features (1) |
|
The following is not guaranteed.
|
| Features (2) |
 |
 |
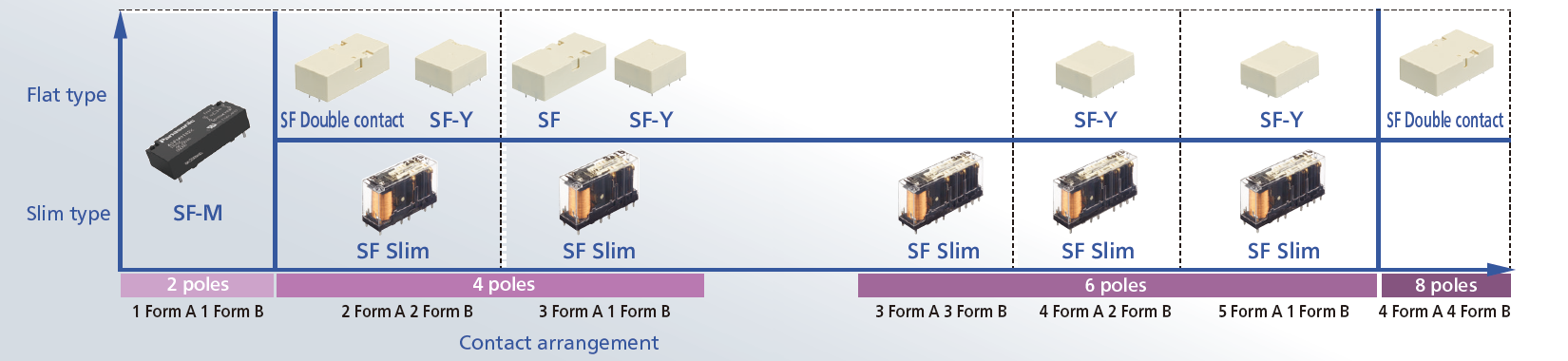
Product Lineup
Rich lineup
Specifications
| Product name | SF-M | SF Slim | SF-Y | SF | SF Double contact |
| Structure | |||||
| Contact arrangement |
1 Form A 1 Form B | 4 poles: 2 Form A 2 Form B, 3 Form A 1 Form B 6 poles: 4 Form A 2 Form B, 5 Form A 1 Form B, 3 Form A 3 Form B |
4 poles: 2 Form A 2 Form B, 3 Form A 1 Form B 6 poles: 4 Form A 2 Form B, 5 Form A 1 Form B |
3 Form A 1 Form B | 2 Form A 2 Form B, 4 Form A 4 Form B |
| Contact rating |
N.C. : 4 A 250 V AC 30 V DC N.O. : 6 A 250 V AC 30 V DC |
6 A 250 V AC 30 V DC | 6 A 250 V AC 30 V DC | 6 A 250 V AC 30 V DC | 6 A 250 V AC 30 V DC |
| Min. switching load (reference value) |
1 mA 10 V DC | 1 mA 5 V DC | 10 mA 10 V DC | 100 mA 5 V DC | 100 mA 5 V DC |
| Rated operating power |
Operating: 270 mW Holding: 100 mW |
4 poles: 360 mW 6 poles: 500 mW |
670 mW | 500 mW | 500 mW |
| Rated coil voltage |
3, 5, 12, 16, 18, 21, 24 V DC | 12, 24, 48 V DC | 5, 12, 16, 18, 21, 24 VDC | 5, 12, 24, 48, 60 V DC | 5, 12, 24, 48, 60 V DC |
| Ambient temperature |
-40°C to +85°C | -40°C to +85°C | -40°C to +70°C | -40°C to +70°C | -40°C to +70°C |
| Safety standard |
UL/C-UL, TÜV | UL/C-UL, TÜV, Korean S, CQC | UL/C-UL, TÜV | UL/C-UL, TÜV | UL/C-UL, TÜV |
| Website | ▷ Product page ▷ Catalog Download |
▷ Product page ▷ Catalog Download |
▷ Product page ▷ Catalog Download |
▷ Product page ▷ Catalog Download |
▷ Product page ▷ Catalog Download |
Application Introduction
Self-holding Circuit during Emergency Stop
■ Typical example Production equipment: Emergency stop circuit
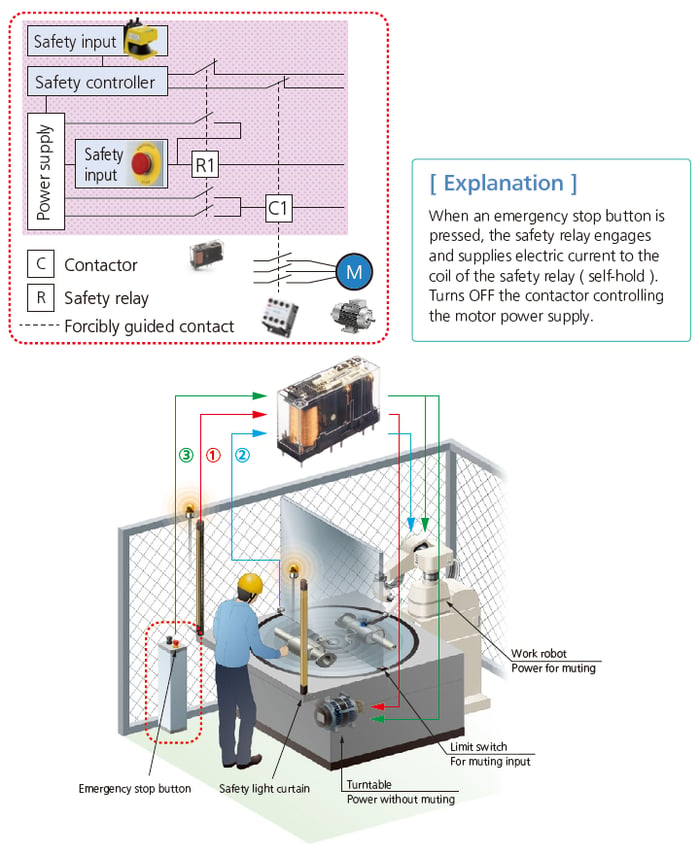
Detect Abnormalities and Stop the System
■ Typical example Production equipment: Abnormality detection and stop circuit when contact welding occurs.
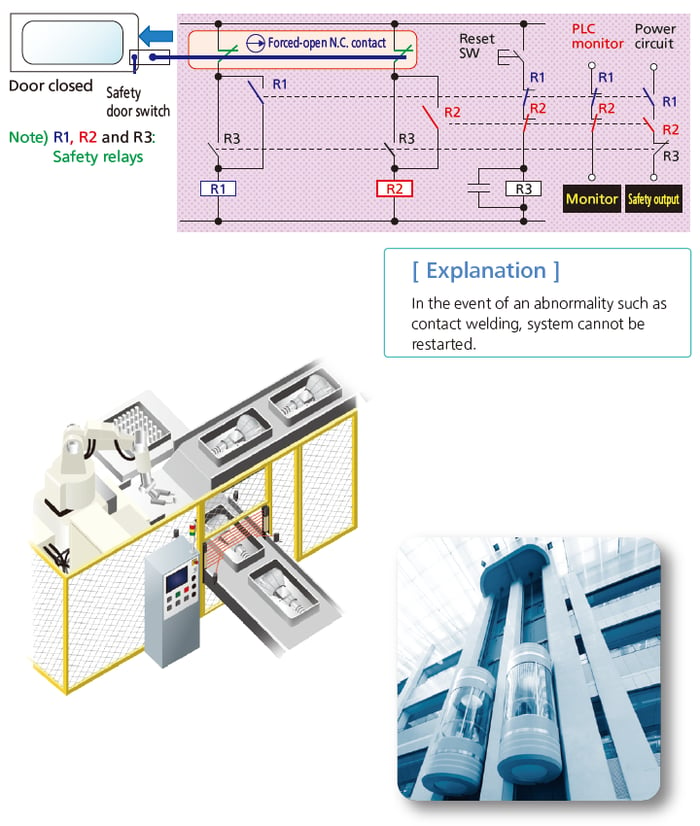
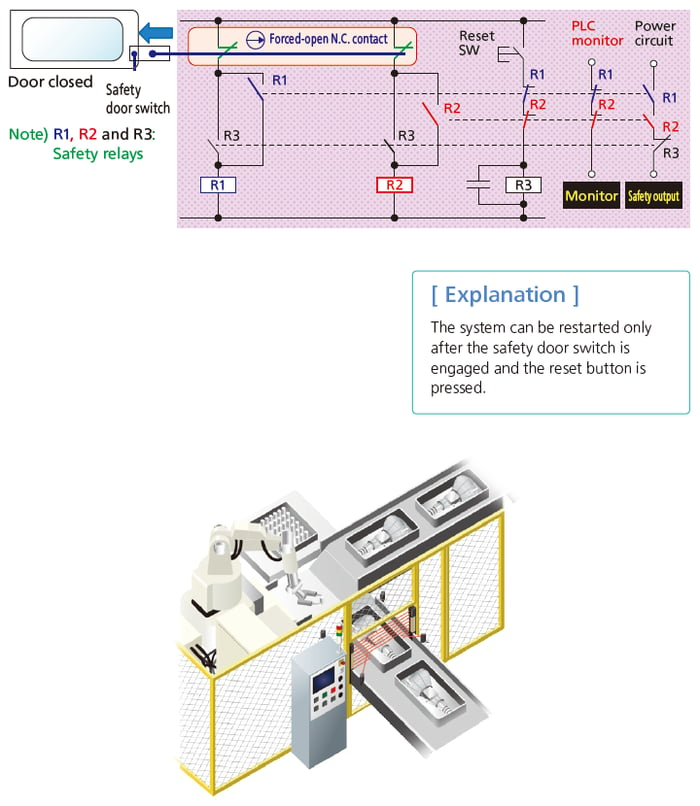
Ensuring Safety through Sequence Control
■ Typical example Production equipment: Sequence circuit
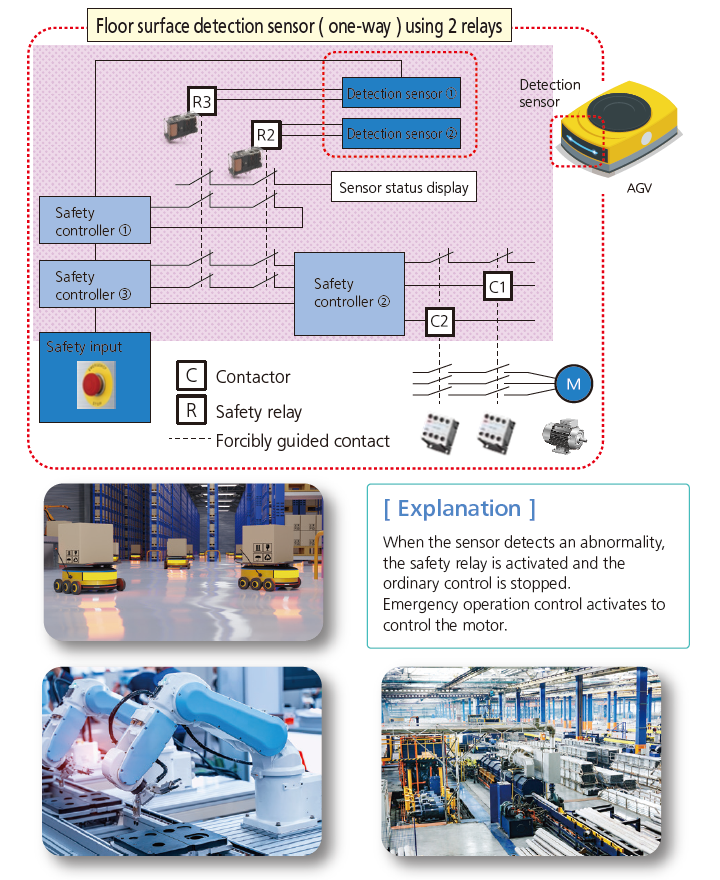
Coordinated ON / OFF of Control Circuit that must not Operate Simultaneously
■ Typical example Production equipment: Switching circuit
Safety relays only → Enable realization of Equivalent Safety Circuits using Safety Relays together with Electronic Circuit
■ Typical example Production equipment: Abnormality detection circuit
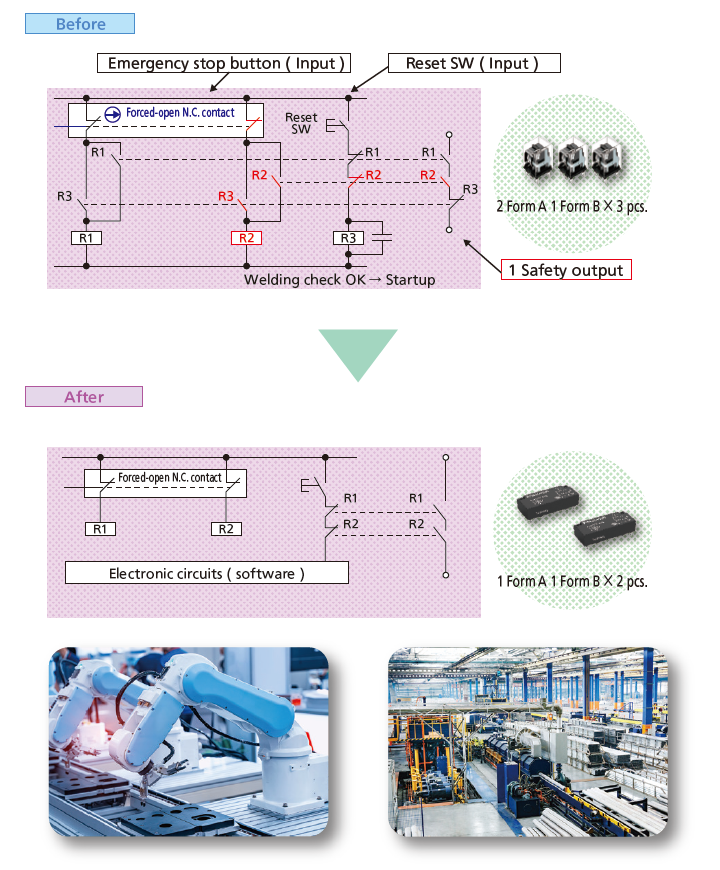
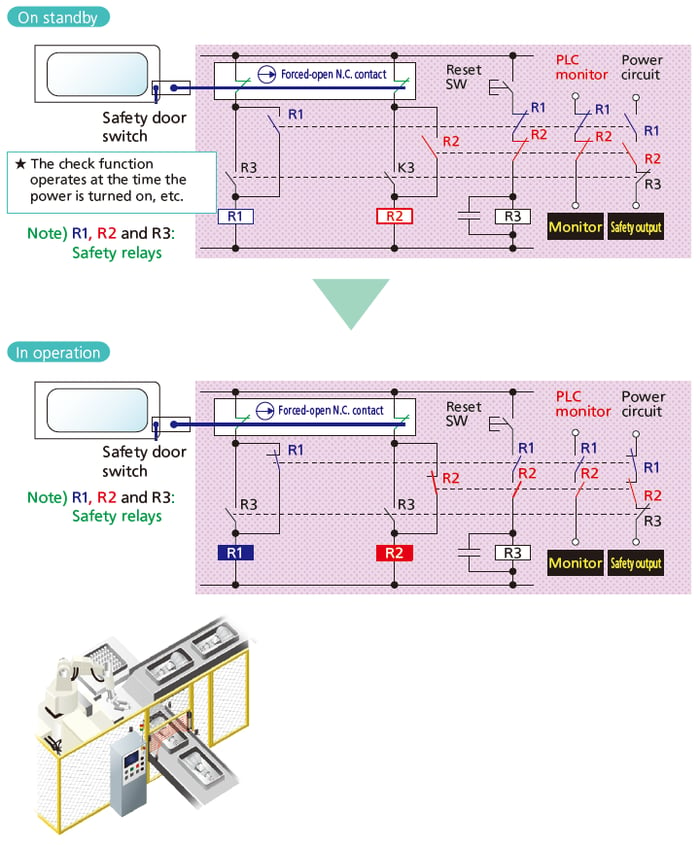
Safety Circuit Construction using Safety Relays and Examples of Functions
■ Typical example Production equipment: Safety door