This article shows technical terms related to relays.
Contacts
1.Contact structure
The contact structure refers to the contact mechanism and number of contacts making up a contact circuit.
2.Contact symbols
| Form A contact (normally opened contact) |
Form B contact (normally closed contact) |
Form C contact (change over contact) |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
Form A contact is also referred to as an N.O. contact or make contacts.
Form B contact is also referred to as an N.C. contact or break contact.
Form C contact is also referred to as a change over contacts or transfer contact.
3.MBB contact
An MBB contact is a contact mechanism in which Form A contacts (N.O opened contact) is closed before Form B contacts (N.C. contact) is opened. "MBB contact" stands for "make-before-break" contact.
4.Rated switching Power
The rated control capacity is a reference value determining specification of an opening/closing section. It is expressed as a combination of a contact voltage and current.
5.Maximum switching voltage
The maximum switching voltage refers to the maximum allowable voltage for opening/closing a contact. When using a relay, please make sure that the input voltage to the relay do not exceed this value.
6.Maximum switching current
The maximum switching current refers to the maximum allowable current for opening/closing a contact. When using a relay, please to make sure that the input current to the relay does not exceed this value.
7.Maximum switching power
The maximum switching power refers to the maximum allowable power with which a contact can be opened and closed without any problem. The maximum switching power is expressed in watts in a DC circuit, and in volt-amperes in an AC circuit. When using a relay, please to make sure that the input power to the relay does not exceed this value.
8.Maximum switching capacity
The maximum switching capacity represents the relationship between the maximum allowable contact power, maximum allowable contact voltage, and maximum allowable contact current. The maximum switching capacities of various types of relays are listed as maximum contact capacity data. This graph should show maximum the contact current and voltage. For example, if the contact voltage is already given, you can find the maximum contact current by checking the intersection between the voltage value, shown using the vertical axis, and the maximum switching power.
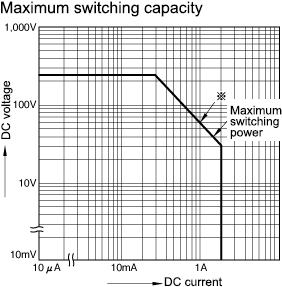
(Example) In the above graph, when the contact voltage is 60 V DC, the maximum contact current is 1 A. Please note that these values are measured using resistor load. Please check actual load before use.
9.Minimum switching capacity
This is the lowest limit of relays to switch low level load. The reliability of this lower limit value varies depending on the switching frequency, ambient conditions, changes in the required contact resistance, the absolute value of the contact resistance. In case analog micro-load control or a contact resistance of 100 mΩ or less to be used, please choose a relay with an AgPd contact. Please contact our sales representative before using such relays.
10.Contact resistance
This is the resistance at a contact point where contacts are touching each other, combination of resistances of a terminal and contact spring. The contact resistance is measured using method indicated in the following chart. Measurement currents in this tests are defined in the table below (according to JIS C5442).
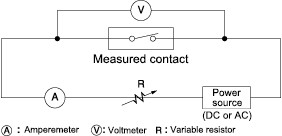
Test currents
| Rated contact current or switching current (A) | Test current (mA) |
|---|---|
| 0.01 or less | 1 |
| 0.01 or more and less than 0.1 | 10 |
| 0.1 or more and less than 1 | 100 |
| 1 or more | 1,000 |
Unless otherwise specified, the contact resistance is measured using a YHP 4328A milliohmmeter. In the case of a relay with contact rating of 1 A or more, measure using voltage-drop method at DC 6V 1A.
11.Maximum carrying current
This is current that contacts pass can continuously in operating state, without increasing the temperature of the contacts and other parts above their limit temperature.
12.Capacitance
This value measured between terminals at conditions of 1 kHz and 20°C.





